Difference between revisions of "MD Store"
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
For now we assume that the MD Store will implement 3 interfaces: | For now we assume that the MD Store will implement 3 interfaces: | ||
* to manage the metadata updates and synchronize with metadata from the origin repository | * MDStore Basic interface - to manage the metadata updates and synchronize with metadata from the origin repository | ||
* SPARQL | * MDStore search interface - SPARQL endpoint | ||
* | * MDStore linked data publishing interface | ||
During implementation this may possibly change, e.g. make linked data interface as a separate service. At present we see no need for it. | During implementation this may possibly change, e.g. make linked data interface as a separate service. At present we see no need for it. | ||
Revision as of 10:12, 29 July 2010
Introduction[edit]
The MD Store is a triple store for medatada storage and management. The MD Store manages resources which are items or containers in an eSciDoc Repository. The MDStore is designed to be used independently from eSciDoc Repository (in case such a need arises) or in relation with another, non-eSciDoc repository. The following scenarios are covered with the MD Store:
- batch metadata update
- linked data publishing
Technology[edit]
- The triple store technology is Jena SDB (TDB doesn't support transactions)
Data model[edit]
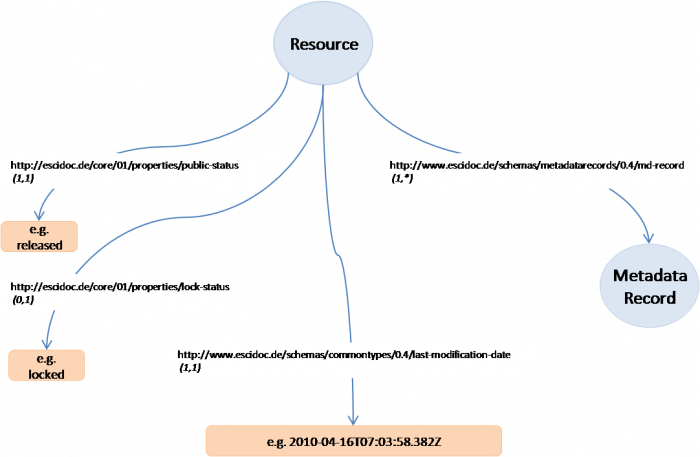
Draft visualization of how resources would be stored in the MDStore is given in the mage below:
Mapping to eSciDoc resources[edit]
- Resource can be any eSciDoc resource of type Item or Container.
- Metadata Record is the full content of a metadata record that is stored externally from eSciDoc Items and Containers. The eSciDoc items/containers would only reference the metadata record stored in the MDStore. For this purpose for each metadata record of an Item or a Container there is a special (RDF/XML) metadata profile that links further to the metadata record stored in the MDStore.
Interface[edit]
For now we assume that the MD Store will implement 3 interfaces:
- MDStore Basic interface - to manage the metadata updates and synchronize with metadata from the origin repository
- MDStore search interface - SPARQL endpoint
- MDStore linked data publishing interface
During implementation this may possibly change, e.g. make linked data interface as a separate service. At present we see no need for it.
MDStore basic interface[edit]
The MD Store implements a REST interface. The REST interface methods are:
- GET: retrieves the requested resource
- POST: create a new resource
- PUT: Updates a resource
- DELETE: Deletes a resource
MDStore search interface[edit]
- is the SPARQL endpoint coming from Jena Joseki
URL definition[edit]
Base URL[edit]
- Base URL of the core-service instance is appended with the URL of the new-service
<core-service-url>/md-store
e.g.
http://coreservice.mpdl.mpg.de/md-store
Interface Methods URL[edit]
- For retrieval of the complete resource from the MD store (properties + all metadata record graphs)
<base-url>/<resource-id>
e.g.
<base-url>/escidoc:1234
- For all metadata records graph (NOTE: there can be several metadata records managed in the MD Store for a resource)
<base-url>/<resource-id>/md-records
e.g.
<base-url>/escidoc:1234/md-records
- For single metadata record graph
<base-url>/<resource-id>/md-records/md-record/<md-record-id>
e.g.
<base-url>/escidoc:1234/md-records/md-record/escidoc
- For properties graph
<base-url>/<resource-id>/properties
e.g.
<base-url>/escidoc:1234/properties
MDStore linked data interface[edit]
- TBD
Data Model[edit]
- The MD Store defines 2 rdf graphs:
- Metadata graphs, where metadada triples are stored
- Property graphs with following properties:
- context-id
- public-status
- lock-status
- content-model-id
- last-modification-date
- created-by
- modified-by
- version-status
- Note: the names of the properties are same as in eSciDoc core. However, in case when eSciDoc Core is not used, these may be set-up by the external system
Questions[edit]
- shall the interface methods understand the resource version-id?
- three alternatives could be implemented:
- content-stream
- is indeed for binary content only (together with the item object, must be base-64 encoded, most probably not applicable)
- md-record - good as in this case we could deal with items, containers ... even originally considered as cumbersome, may be good approach e.g.
- create new MD-Profile (Externally-reference
- externally-referenced component
- content-stream
- the Model itself-> when things come from CoNE -> we treat them as CoNE resources or not?
- MDStore would not contain any descriptive metadata from CoNE in addition, only a link to CoNE resource? (cleaner)
- CoNE changes?
- MDStpore would contain additional descriptive metadata of a CoNE Resource (provided by the end user) and a link to CoNE Resource?
- MDStore would not contain any descriptive metadata from CoNE in addition, only a link to CoNE resource? (cleaner)
Architecture[edit]
- eSciDoc: The MD Store uses eSciDoc security management (AA)
- It should be generic to enable other services to log in into MDstore