DC Application Profile
This page is to summarize the DCMI specifications and concepts of DC Metadata profiles and howto create them.
DCMI Description Set Profile[edit]
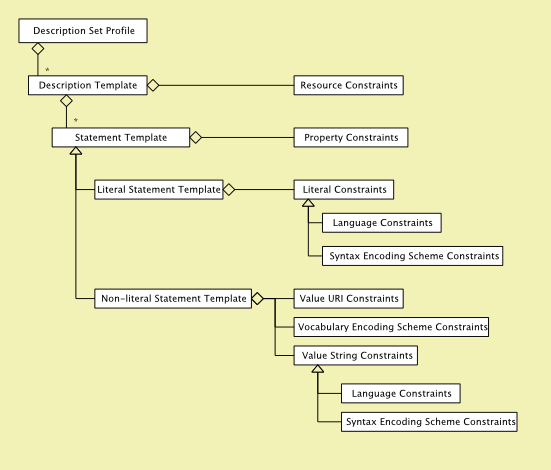
Resources, properties and values are given in a Description set which can be defined in a Description Set Profile (DSP). A Description Set Profile (DSP) basically consists of Templates and Constraints. Templates are to express structures and Constraints limit those structures. The following graphic from DCMI shows the basic structure of a DSP:
Templates[edit]
In the left part of the graphic all kinds of Templates are given. Templates describing
- resources (Description Template)
- statements or properties (Statement Template, Literal Statement Template, Non-literal Statement Template)
Constraints[edit]
The right part of the graphic shows the different kinds of constraints that can occur in a DSP.
Constraints are used to define limitations on
- resources e.g. only resources of type foaf:person are allowed (Resource Constraints)
- properties e.g. a person has a property called foaf:name (Property Constraints)
- two ways: giving an explicit list of allowed properties, requiring the property to be a sub-property of a given property
- values e.g. the value of a special property must be a Literal (kinds of Literal Constraints, Value Constraints and Vocabulary Encoding Schemes)
Terms and Definitions[edit]
Resourse
Statement Literal An entity which uses a Unicode string as a lexical form, together with an optional language tag or datatype, to denote a resource (i.e. "literal" as defined by RDF [RDF].
Dublin Core Abstract Model A generic syntax for metadata records.
DCMI syntax guidelines/DCMI Encodings Which use the generic syntax for concrete implementation encodings.
DCMI Application Profile (DCAP)[edit]
What is DCAP?[edit]
Dublin Core Application Profile (DCAP) is a description and specification of the metadata used in a particular application. It consists of one or more documents and contains:
- Functional Requirements of the application (mandatory)
- Domain Model - types of things that are described my metadata and relationships (mandatory)
- Description Set Profile (DSP) - catalogue with metdata terms and constraints (mandatory)
- Usage Guideline - describes how to apply the application profile, how the used properties are intended to be used in the application context etc.(optional)
- Encoding Syntax Guidelines and Data Formats - which syntax/format is used to encode the data (optional)
Why DCAP?[edit]
- Different applications have different metadata needs and use several formats and vocabularies.
- need to provide metadata across applications and semantic interoperability.
Approach:
- DCAP is a framework that meets specific application needs while providing semantic interoperability with other applications on the basis of globally defined vocabularies and models (DCMI Profile Guidelines).
- DCAP is generic and you can use it with any metadata terms that are defined in accordance with the RDF.
DCMI Abstract Model[edit]
What is DCAM?[edit]
- it is an information model that specifies the components and constructs used in DC metadata
- it defines how the components can be combined to create information structures
- it is syntax independent
- it uses the RDF concepts
DCAM deals with three basic concepts:
- DCMI Resource Model
- DCMI Description Set Model
- DCMI Vocabulary Model
The DCMI Resource Model[edit]
What is a Resource?[edit]
- DCMI uses the RDF idea of a resource: RDF defines a resource as anything that is identifiable by a URI reference [1]
- each resource is described by one or more property-value pairs e.g. dc:creator "Hans Müller"
- a property-value pair consists of one property (e.g. dc:creator) and one value (e.g. "Hans Müller")
- each value can be a non-literal value (or resource: a physical, digital or conceptual entity) or a literal value
- a literal is a Unicode String with an optional language tag or datatype e.g. "2005-03-06"^^xs:date
The DCMI Description Set Model[edit]
What is a Description Set?[edit]
- set of one or more descriptions (each description describes a single resource)
What is a Description?[edit]
- description is made of one or more statements (about one resource) and zero or one URI
What is a Statement?[edit]
- instance of a property-value pair (property-URI and a value), e.g. dc:creator "Max Müller"
The DCMI Vocabulary Model[edit]
DCMI Process of Building an DCAP[edit]
Step 1: Defining Functional Requirements[edit]
- involved people: service manager, experts in the material being used, technical application developers and potential endusers of the service
- goal:
- content: general goals and specific tasks.
- user tasks that must be supported
- developer needs
Ideally, functional requirements should address the needs of metadata creators, resource users, and application developers so that the resulting application fully supports the needs of the community
- methodologies: e.g. business process modeling, methods for visualizing requirements (such as UML), definition of use cases and scenarios for a particular application
Step 2: Selecting or Developing a Domain Model[edit]
The Domain Model describes the entities or things appear in the application and the relationships between them. Picture 2 shows a sample.

Step 3: Selecting or Defining Metadata Terms[edit]
In this step all entities identified by building the Domain Model have to be described using Metadata Terms as properties.
Define a Description Set for each entity of the Domain Model[edit]
Each entity of the Domain Model is described by a Description Set [1], which contains of a list of Statements. A Statement is a property-value surrogate pair (e.g. dc:title = SimpleLiteral).
Sample:
Description Set: Book
Statement: title
Statement: creator
Statement: date
...
Assign properties to Metadata Terms[edit]
Each Statement-property needs to be assigned to a Metadata Term. If no pre-defined term fits to the property intention, create a new one. Within a Description Set Metadata Vocabularies can be mixed up. Most metadata vocabularies are intended for a special purpose or special kinds of entities.
Sample:
Description Set: Book
Statement: title
Property: http://purl.org/dc/terms/title
Statement: creator
Property: http://purl.org/dc/terms/creator
...
Describe the property value[edit]
The property value have to be configured by considering the following issues:
- is the value a free text or controlled vocabulary
- does it have a special syntax format (Syntax Encoding Scheme, e.g. YYYY-MM-DD for date)
- for controlled vocabulary: is there already a pre-defined list available?
- Do you want to use the complete list as it is or use a customized version with extended or limited elements?
- is the value a single string value like "text" (literal) or is it a composition of more values like "name, address, email" (non-literal)?
- is it intended to store a URI to the value or refer to a value description?
Step 4: Designing the Metadata Record with a Description Set Profile[edit]
- Description Set Profile (DSP) describes the metadata record in detail
- DSP is a constraint language for DCAPs
- DSPs are based on the Description Set Model, which is part of the DCAM
- DSP contains one Description Template for each thing/entity in the domain model
Sample:
DescriptionSet: MyExample
Description template: Book
minimum = 1; maximum = 1
Statement template: title
minimum = 1; maximum = 1
Property: http://purl.org/dc/terms/title
Step 5: Usage Guidelines[edit]
- instructions to the person who creates the metadata records
- the "how" and "why"
- explain each property and decisions regarding the metadata record
- some infos are also in the DSP, but more human-readable
- Usage guideline can be included in DSP or a separate document
Step 6: Syntax Guidelines[edit]
Syntax Guidelines should help the developer to implement the Application Profile in a specific language. The DCMI has developed/is developing some encoding guidelines [2] in HTML/XHTML, XML, RDF/XML. But any other syntax can be used as long as the data conforms to the foundation standards defined in DCAP.
Appendix: Metadata Vocabularies[edit]
The following links refer to specifications of some common metadata vocabularies sorted by their purpose:
- Publications and Documents
- Person and Organization Metadata
- Photo Metadata
External Links[edit]
- Description Set Profiles: A constraint language for Dublin Core Application Profiles
- DCMI Abstract Model
- EPrints Application Profile
References[edit]
DCAM
Powell, Andy, Mikael Nilsson, Ambjörn Naeve, Pete Johnston and Thomas Baker. DCMI Abstract Model. DCMI Recommendation. June 2007.
http://dublincore.org/documents/2007/06/04/abstract-model/
DSP
Mikael Nilsson. DCMI Description Set Profile Model. Working Draft, December 2007.
http://dublincore.org/architecturewiki/DescriptionSetProfile
Generic handling of metadata MPDL Draft