Difference between revisions of "OAI-ORE"
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
===Possible new Features=== | ===Possible new Features=== | ||
* One step towards the 'research data continuum'? If we can model faces, ViRR, PubMan data in ore, we can easily create new Aggregations containing data from different solutions. | * One step towards the 'research data continuum'? If we can model faces, ViRR, PubMan data in ore, we can easily create new Aggregations containing data from different solutions. | ||
::i'd think this is basically thanks to RDF, not ore. | |||
* Visualize data with Foreside | * Visualize data with Foreside | ||
Revision as of 17:46, 26 June 2009
http://www.openarchives.org/ore/logos/ore_logo_e_128.png Open Archives Initiative - Object Reuse and Exchange
General[edit]
OAI-ORE is a standard to describe and identify aggregations on the web. Taking a publication as an example, it mostly consists of multiple resources (publisher pdf, supplementary material, metadata etc.), therefore what we 'see' as an publication is actually the aggregation of multiple resources.
Aggregations should be modelled in respect of the core foundations of the Web
- Resource, an item of interest.
- URI, a global identifier for a Resource.
- Representation
- Link, a directed connection between two Resources.
Basic Principles[edit]
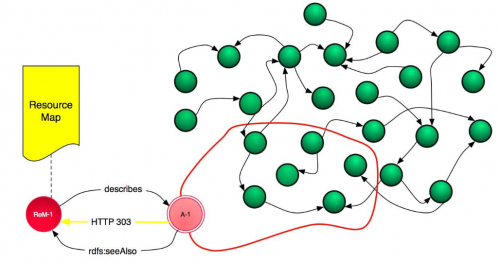
Image from: http://www.slideshare.net/hvdsomp/the-oaiore-interoperability-framework
Aggregation (A)[edit]
Resource Map (ReM)[edit]
An information resource that describes an aggregation
Data model[edit]
RDF Graph using name spaces:
- dc (http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/)
- dcterms (http://purl.org/dc/terms/)
- foaf (http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/)
- ore (http://www.openarchives.org/ore/terms/)
- owl (http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#)
- rdf (http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#)
Advantages[edit]
General[edit]
- Improve interoperability
- Using a (soon?) standard for modelling our relations
- Detection and processing of relation information, within and outside eSciDoc
- Following the principles of Linked Data (share structured data on the Web)
- Addressing Cool URI and content negotiation
Possible new Features[edit]
- One step towards the 'research data continuum'? If we can model faces, ViRR, PubMan data in ore, we can easily create new Aggregations containing data from different solutions.
- i'd think this is basically thanks to RDF, not ore.
- Visualize data with Foreside
Tools[edit]
- Java Library (for constructing, parsing, manipulating and serializing OAI-ORE Resource Maps. ATOM, RDF/XML, N3, N-Triples, Turtle and RDFa)
- Foreside Explorer (Visualization of Relations)
Steps[edit]
The basic steps to integrate OAI-ORE to eSciDoc (regarding publication data for start) would be:
- Create mapping from eSciDoc Publication Item to ore
- Create mapping from ore to eSciDoc Publication Item
- Make sure that every resource has its own URI
- Expose oai_ore over OAI-PMH
- Implement http part
- Enable SWORD deposit of ore data
OAI-ORE in use[edit]
This is just an extract of systems supporting OAI-ORE:
- EPrints
- Fedora
- DSpace
- Microsoft Zentity
- MyExperiment.org
- arXiv.org
- Flickr
- Oxford Research Archive
- Word Press
- Amazon