Difference between revisions of "DC Application Profile"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This page is to summarize the DC specifications and concepts of DC Metadata profiles and howto create them. | This page is to summarize the DC specifications and concepts of DC Metadata profiles and howto create them. | ||
== | ==DCMI Description Set Profile== | ||
Resources, properties and values are given in a Description set which can be defined in a Description Set Profile (DSP). | Resources, properties and values are given in a Description set which can be defined in a Description Set Profile (DSP). | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
Literal | Literal | ||
== | ==DCMI Application Profile== | ||
== | ==DCMI Abstract Model== | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 13:16, 7 November 2008
This page is to summarize the DC specifications and concepts of DC Metadata profiles and howto create them.
DCMI Description Set Profile[edit]
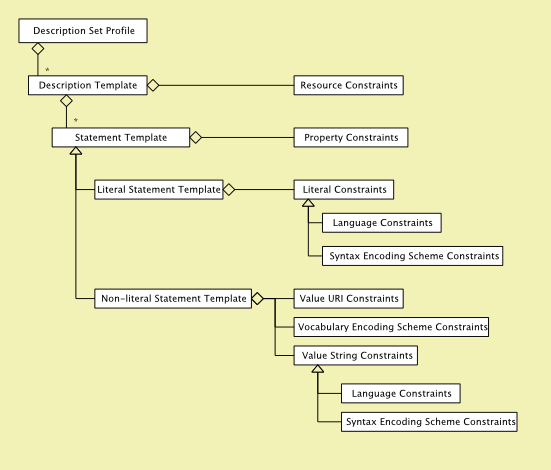
Resources, properties and values are given in a Description set which can be defined in a Description Set Profile (DSP). A Description Set Profile (DSP) basically consists of Templates and Constraints. Templates are to express structures and Constraints limit those structures. The following graphic from DCMI shows the basic structure of a DSP:
Templates[edit]
In the left part of the graphic all kinds of Templates are given. Templates describing
- resources (Description Template)
- statements or properties (Statement Template, Literal Statement Template, Non-literal Statement Template)
Constraints[edit]
The right part of the graphic shows the different kinds of constraints that can occur in a DSP.
Constraints are used to define limitations on
- resources e.g. only resources of type foaf:person are allowed (Resource Constraints)
- properties e.g. a person has a property called foaf:name (Property Constraints)
- two ways: giving an explicit list of allowed properties, requiring the property to be a sub-property of a given property
- values e.g. the value of a special property must be a Literal (kinds of Literal Constraints, Value Constraints and Vocabulary Encoding Schemes)
Definitions[edit]
Resourse
Statement Literal