Living Sources in Lexical Description
Summary[edit]
Living Sources is an infrastructure for publishing scientific data. There are many general issues concerning the publication of data (in contrast to the publication of results) that are applicable to most scientific fields (specifically, issues like persistence, quality control and scientific recognition). The Living Sources concept aims to address these problems, so different fields of scientific inquiry can profit from the solutions proposed. The general plan of publishing data will be approached through a concrete case, namely the Living Sources in Lexical Description, an online data-journal for the publication of dictionaries of the world's languages.
The Living Sources concept[edit]
Current situation[edit]
In contrast to the common practice of publishing and discussing research results, currently most scientists do not disclose the underlying research data. They do not make them available to a wider audience because of various reasons, like:
- failure to see wider applicability of data ("Why would anybody be interested in this?")
- insufficient quality (e.g. the data collection is not finished, it is not properly cross-checked, or the data is not complete)
- fear of plagiarism (others might not properly acknowledge the data)
- loss of control over interpretation (others might misunderstand the data, with undeserved blame being cast on the original creator of the data)
- loss of primacy of discovery (others might come up with important discoveries that the original creator also observed, but did not have time to work out and publish)
- lack of suitable publications to publish the data (most publishers are not interested to publish large tables with raw data)
- lack of technical knowledge how to make data available
- limited scientific recognition for making data available
All these - completely legitimate - reasons lead to the current situation in which data are mostly unavailable for inspection and scientific scrutiny, unavailable for reanalysis, and unavailable for meta-analysis. When much more (raw) data would be available, many new possibilities for research, both within disciplines but also across disciplines, will become possible. The goal of the Living Sources project is to provide an environment for the scientific publication of data that addresses these provisos.
Prospects[edit]
Recent developments in computational infrastructure ("web 2.0") are showing the possibility for new kinds of information exchange. Living Sources will be an online repository of information created for and by scientists, tailored to the goals and needs of these scientists. To reach this goal, the concept of Living Sources will tackle problems that are general enough to be of importance to many field on inquiry:
- persistence of data (storage and archiving)
- systems of quality control ("peer review")
- securing of scientific recognition and citability
The electronic format of publication offers various additional possibilities:
- incremental publications (corrections and additions possible, which is difficult for traditional forms of publications)
- comments on and citation of individual datapoints (micro-publication too small for traditional forms of publication)
- open peer review schemes
- addition of digitalized legacy material to supplement the newly published data
- persistence of data through grid-like backup
Strategy[edit]
Living Sources will not attempt to force scientists to adapt to new paradigms of how to deal with data. It will function more as a service to those (sub)fields that have a need for data publication and dissemination. An instance of the Living Sources concept will be in need of:
- Availability of data with high level quality
- Support from scientists in the field
- An organisational boards (for technical checks and organisation of field)
- Editorial boards and active engagement of scientists in the peer review (content check)
There are at least two complementary scenarios for the application of the Living Sources concept. First, the construction of a dedicated technical infrastructure which enhances the usability of data. This should be a "one stop shop" for scientists who look for a hosting environment, including all features needed for usage and deployment of such a system (including, e.g., user interfaces for editors, casual browsers and power users, searchability, persistent data storage, etc.). Second, Living Sources aims to set standards for the structure of data portals (like data journals or data archives) as for issues of citation and quality control. This is specifically geared towards groups of scientists who want to keep a strong hold on their data can build their own systems, that are still interoperable with the dedicated Living Sources infrastructure.
Separating publication from quality control[edit]
An important new possibility for scientific publishing, offered by the online electronic format, is that publication and quality control can be separated. In a publication system where each publication is costly, the quality control has to precede the physical publication. In contrast, in electronic form, the cost of each publication if small (the main costs relate to the up keeping of the overall system, not to the individual item published). This allows for a system in which publication itself (i.e "making available") can happen independent of the assessment of the quality ("peer review").
In the context of Living Sources, we would like to encourage people to publish ("make available") smaller amounts of data, or even incomplete data, to the (scientific) public. However, such small or incomplete data sets of course should be distinguished from large and finely annotated data collections. To allow for different kinds of publications, some kind of stratification is needed. This stratification of publication will happen through the peer review system. The data in Living Sources will be stratified in four different stages, compared here with traditional article publication:
| Stage | Traditional Article | Availability to outsiders in traditional publication | Living Sources | Availability to outsiders in Living Sources | Scientific Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Incomplete Text | unavailable | Data in closed personal workspace | unavailable | draft |
| 2 | Submission | unavailable | Data accessible to others | available | manuscript |
| 3 | Submission | unavailable | Technically correct published data | available | self-publication |
| 4 | Peer-reviewed | available | Peer-reviewed data | available | scientific publication |
There are two main differences between the structure of Living Sources and traditional scientific publication. First, the difference between Stage 2 ("manuscript") and Stage 3 ("self-publication") is newly added especially for Living Sources, and, second, the content in both these stages is openly available in Living Sources. In traditional publication format, these two stages together are combined as a non-peer-reviewed manuscripts, which are normally not available to outsiders. In recent years, such manuscripts are made available more and more in the form of self-publication, either by using one's personal webpage or a manuscript archive, like arXiv.org or ling.auf.net/lingBuzz. In this sense, Living Sources is just following the current trend of making data available before it has been checked by peers.
The new distinction between Stage 2 and 3 becomes necessary because Living Sources has to deal with structured content that has to be computer-readable. In this context, it is of central importance to assure that the form of the publication is correct (e.g. right formatting, sufficient metadata, etc.). Only in a second check, the content of the data will be checked. To some extent, this distinction can be compared to a system in which traditional articles undergo two separate controls: one control which checks the spelling and grammar of the article, and judges whether the style is sufficient for the argumentation to be understood, and another control which checks whether the content is deemed interesting enough to be passed on to the rest of academia. Traditionally, these two checks are combined into the peer-review system (many journals will do the first check separately in the form of an editorial check, which prevents badly written articles to be passed on to the peer-review), which is not visible for outsiders. For humanly readable texts it is actually a good idea to restrict the amount of available texts in this way: there is already way to much text available for scientists to read. However, a large quantity of technically correctly published structured data is much easier dealt with. In this realm, it seems more profitable to have a bit too much data available, than too little.
A very important consequence of this structure, that has to be clearly pointed out to possible content providers, is that data in Stage 2 ("manuscript" level) cannot be retracted anymore. Once it is made openly available, it is citable and has to be kept accessible for everybody. Of course, an author can make corrections, or even add a clearly visible sign to the data saying that, for example, the author discovered only after the data has been made available that there is a potential flaw in the data, and does not have time/money/possibility to correct the error. All of this will happen openly, and that might scare some scientists. It will be part of the community building to explain these scientists that possible flaws are inherent to data collection.
Formal structure[edit]
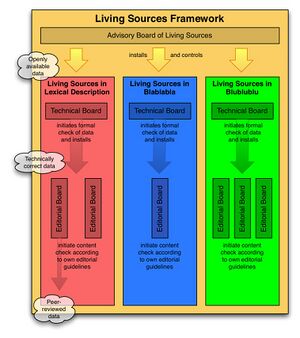
The framework of Living Sources will have three different kinds of official bodies:
- One Advisory Board for the whole framework of Living Sources
- A Technical Board for each instance of Living Sources, for example "Living Sources in Lexical Description"
- Various Editorial Board for each peer review process within an instance of Living Sources
The framework of Living Sources is explicitly formulated to allow for future expansion into different fields of scientific investigation. The Advisory Board has the responsibility to oversee such expansion in the future. Within the current project, only one instance of the Living Sources framework is initiated, so the advisory board will not have many day-to-day obligations. However, when this first instance is successful, many other groups of scientist might follow. Already within the field of linguistic documentation and description there is a clear need for organizations like "Living Sources in Grammatical Description" or "Living Sources in Annotated Texts".
Any such instance of the Living Sources framework will need a Technical Board, which specifies the formal prerequisites for the data to be published in it's context (i.e. what kind of data are allowed, what are the minimal requirements for the data, which metadata is needed, etc.). The Technical Board is also responsible for checking their own requirement. When a set of data meets the requirements, it has passed the formal phase of the quality control.
The next step of the quality control is a check of the content, which is performed by an Editorial Board. This board is in principle independent of the Technical Board, though there might be personal overlap. It is very well possible to have an instance of Living Sources without any Editorial Board, or to have multiple Editorial Boards alongside each other, with different criteria to evaluate the data.
Living Sources in Lexical Description[edit]
Scientific scope[edit]
Words are of prime interest to linguists and the general audience alike. Various branches of linguistics are interested in well-organized and cross-searchable lexical resources, like:
- Lexicography and terminology research
- Description and documentation of endangered languages
- Dialectology
- Ethnolinguistics
- Historical linguistics
- Computational linguistics
- Psycholinguistics
Also, in the context of the recent movement in linguistics to recognize constructions (including both "set expressions" and "grammatical structures") as language-particular entities on a par with lexical items ("words"), the infrastructure for lexical resources can be expanded to a much larger scope of language description in the future.
The Living Sources in Lexical Description is the first implementation of the Living Sources framework. It is specifically geared towards the publication of dictionaries and other lexical resourced of the world's languages. It will be primarily focussed on lexical resources of lesser studies and often endangered languages, offering specialists for such languages to publish their resources for which there is mostly no real interest among traditional publishers. The result is that many of the people working in the context of language documentation and description have a great amount of scientifically highly valuable lexical data that mostly does not leave their desks. Even if they are lucky enough to find a publisher for a dictionary, this will only be for very particular particular kind of data, namely not too little (as that will not make a nice book), nor too much (because that will not fit into a book). Also, because an offer to publish a dictionary will a one-time event (there is too little demand to allow new editions), there is a strong tendency to push the publication forward as long as possible to let the dictionary be as complete and error-free as possible. So, the traditional publication structure does not really offer a suitable solution for the publication of dictionaries.
Further, the necessity to linearly structure a printed dictionary forces researchers to organize dictionaries in ways that are not always suitable to find entries. In particular, entries are traditionally alphabetically ordered only for the main languages, needing separate dictionaries for a search from the secondary language, or for searching a different string-order (e.g. reversed dictionaries for searching from the back of a word). Also, for languages with many prefixes, an alphabetical dictionary normally forces the inclusion of words with prefixes under the heading of a headword, which makes it difficult to find a word for non-specialist. Conversely, when ordered all separately, all versions of the same headword with different prefixes are difficult to find, making the dictionary far from perfect for more specialistic users. All these arguments show that the printed form is actually a particularly unsuitable format for a dictionary. The advantages of electronic dictionaries are long-known to lexicographers of the world's major languages, though the solutions are normally not accessible for the lesser studies languages.
Also, the published lexical data will offer cross-searchability and cross-annotation, opening up new possibilities for comparative research, like the computer-assisted investigation of cognate words for historical comparison of the world's languages. Today, most historical-comparative research still involves hand-paging through dozens of published dictionaries to find entries that are hidden somewhere inside. To be able to do more comprehensive searches, or even to let dedicated computer algorithms suggest cognate sets, all available data has first to be entered by hand, or (when already available in electronic format) has to be converted into a consistent format.
Living Sources in Lexical Description will offer a better publication platform with much more flexibility, both as to the size of the data, regarding the later extension or corrections of entries, and for searching or using flexible ordering schemes.
Submission and Peer Review[edit]
(for example, complete dictionaries)
For lexical data, we propose a two-layered system. The first level of publication will be called "Words of the World" and consists of a technically correct submissions that do not (yet) have been peer-reviewed. Peer review can (but need not) happen to obtain more scientific recognition, and (if successful) lead to publication in more prestigious series, like "Dictionaries of the World's Languages".
Step 1: Submission[edit]
Submission consists mainly of a technical check by editors.
- data is directly uploaded (in a first phase some technical assistance should be available)
- this leads automatically to an evaluation by to editors (possibly closed, if requested by the author)
- editorial check will be on technical issues and requirements only (data structure, terminology, preface, etc.)
- retraction from peer review at this point still possible, but data remain available (with restricted access if wanted)
- these steps can be iterated until all technical requirements are met
Step 2: Bare publication[edit]
To allow of the availability of data, irrespective of scientific recognition, there should be a level of "bare" publication, with its own brand name.
- data that does not meet all technical requirements can still remain openly available, categorized as Draft
- data that passes the technical check will be announced as published in a special series, for example called Words of the World
Step 3: Review[edit]
There can be different, independent, more prestigious series. Such series simply consist of an editorial board and an active community of peer-reviewers. If that particular scientific sub-community accepts a submission, it can give it's own "seal" of recognition by branding a special series. In the context of lexical data, one could think of series like "Dictionaries of the "World's Languages", "Intercontinental Dictionary Series", "Loanword Typology Wordlists", or "Cognate set collections". The branding and recognition of such series completely depend on the effort and success of the editors and the community or reviewers. Also the criteria to pass the review depend on the editorial board. Initially, only one such brand will be established, namely Dictionaries of the World's Languages.
- if wanted by the author, any technically accepted publication can be opened up for peer review to obtain more scientific recognition
- this peer-review will be time restricted and openly available to the whole community ("open peer review")
- review should be a critical assessment of submission as a whole (i.e. commentary on kind of collection, and on larger samples of submitted data points. For example, someone taking up the obligation to write a peer review will get a set of randomly sampled entries to evaluate.)
- comments on individual entries should be seen separate from commentary on the whole enterprise.
- individual errors/shortcomings can and should be corrected, but should not ban scientific recognition (except of course when the errors are too widespread).
Step 4: Full publication[edit]
On the basis of the reviews, the editors decide on acceptance. After acceptance, the result will be a peer-reviewed dictionary, meaning "the principle of collecting and organising data is good, though there might be discussion about individual items". The submission is then published in the series called "Dictionaries of the World's Languages"
Step 5: Editions/Supplements[edit]
A central part of the Living Sources concept is that published data is changeable. Authors can add and correct data, users can add commentary or additional information. Any larger collections of such additions to the system can be in turn submitted to review (we will not led individual entries through to the review process). The idea is that once a particular author/user has added a lot of new information (i.e an author has added much information to his/her dictionary, or a user has collected many sets of cognates across different languages), such a collection of new information can be given to the scrutiny of the peers, resulting in either a new edition of an available publication, or a supplement to an available publication, or a completely new publication. Such substantially new version should count as publications worthy of being listed on a cv.
Scientific Recognition through Citation[edit]
A central aspect of scientific publication is the organization of scientific recognition. The prime tool to give recognition is science is proper citation. This means that the data in Living Sources in Lexical Description have to be citable to acknowledge each contribution. However, the citation format also has to be practically usable in the context of traditional articles and books (in linguistics, this means there has to be a short in-text citation format, and a more extensive format for the References section, which also should not span more than a few lines). Also, the status of data-publications for CV's has to be considered.
Citations of data in the context of Living Sources have clear parallels to the citation of traditional print media, but there are also some usages of the data that ask for new forms of citation. We distinguish between (at least) four different kinds of citations that people could use: citation of whole submissions, of individual data points, of micro-publications, and of complex collections of many data points originating from various publications. They are to some extent parallel to traditional forms of citation:
- whole submission ↔ book/article
- individual data points ↔ page in a book/article
- micro-publication ↔ personal communication
- collection of data points ↔ multi-author work
Some fictional examples follow, to illustrate how this could possible work (The structure of these example URIs is of course still unsettled.)
Citing whole submissions[edit]
The citation of whole submissions is completely parallel to traditional citation of books and articles. The submission has author, title and a submission data. The "Living Sources in Lexical Description" is like a publisher (though without physical location). The "stamp" is like a series, which might also have a serial number. As being online citations, they of course need a URL and a date. This might, for example, look like:
| Doe, John (2013) Dictionary of Nehali. [Dictionaries of the World's Languages, 3]. Living Sources in Lexical Description. (available online at livingsources.org/dictionaries/doe2013/, accessed on 23 March 2015). |
In-text citation likewise function as normal, e.g. (Doe 2013).
Citing individual data points[edit]
Often just one lexical entry will be cited, or individual points of information available in the databases. This is completely parallel to traditional citation of pages. Each data entity will have its own URI that can be referred to, so it will be possible to add in-text citations like (Doe 2013: foo). In the bibliography only the whole work will be cited, not the individual URI. The URI to the individual data point is a composite of both: "livingsources.org/dictionaries/doe2013/foo/"
| Doe, John (2013) Dictionary of Nehali. [Dictionaries of the World's Languages, 3]. Living Sources in Lexical Description. (available online at livingsources.org/dictionaries/doe2013/, accessed on 23 March 2015). |
Citing micro-publications[edit]
One more unusual situation that comes up in this new medium is the citation of individual comments that have been added by users to an entry, or be individual additions to fill in gaps of an already published source. Such micro-publications should probably be seen as alike to the tradition of "personal communication", meaning that they are cited in-text, but do not turn up in a bibliography. For example, consider the case of a discussion happening on the entry discussed previously (Doe 2013: foo). There are various comments posted in this discussion, and an in-text citation to one of them might look like this: (A. Ash 2015, commenting on Doe 2013: foo/talk/7). In the Bibliography, only the entry on (Doe 2013) turns up, and the link to the comment is like a page number, leading to the URI "livingsources.org/dictionaries/doe2013/foo/talk/7".
| Doe, John (2013) Dictionary of Nehali. [Dictionaries of the World's Languages, 3]. Living Sources in Lexical Description. (available online at livingsources.org/dictionaries/doe2013/, accessed on 23 March 2015). |
Likewise, if, for example, a native speaker would like to add individual words to a published dictionary of his language, such entries could be added on a one-by-one basis, and the citations would work just like comments, e.g. (E. Bare 2014, supplementing Doe 2013: fooxt). If such a person has been adding a lot of new information, he or she might consider submitting the whole collection of additions as a separate publication.
Citing complex collections of data point[edit]
One of the main advantages of electronic resources is the possibility to search for data, possibly resulting in a very complex selection of data, cross-secting multiply submissions. It is very important to have a good system for citing such usage. The closest parallel in traditional citation is citing a multi-author publication. Probably, such citation will work as follows. After creation of a custom data set (e.g. through search and subsequent hand-picked selection), this data set can be saved online, resulting in a URI for the saved data set (e.g. livingsources.org/users/ArthurAsh/savesets/35). With the saved data set comes a receipt that counts the number of selected data points per author, e.g. John Doe (243), Michael Cysouw (67), Sonia Ash (12), D.H.M Broom (2). In the citation of this multi-authored publication, the authors should be ordered according to the amount of data points, and the date would be the date of the saving of the collection. The citation in the bibliography should list all authors, and might look like:
| Doe, John, Michael Cysouw, Sonia Ash, D.H.M. Broom (2015) Custom data collection. Living Sources in Lexical Description. (available at livingsources.org/users/ArthurAsh/savesets/35). |
The form of in text citation might looke like: (Doe et al. 2015), or maybe like: (Doe, Cysouw, Ash et al. 2015), depending on editorial guidelines about citing multi-author works.
Persistence of Data[edit]
- unique IDs, and their usage
- long term archiving
- vision of sustainability (use money from funding agencies for data publication)
Practical Organisation of Project[edit]
A central part of the planned organization is to uniquely identify every word that is submitted to the Living Sources infrastructure. In this way, other users (be it databases of human investigators) can more clearly and readily refer to a particular word.
Submissions should consist of the data in a suitable format (e.g. TMF, LMF, or TEI - concrete decisions are still open on this) with a set of supplementary material. This supplementary material can be considered to be some kind of preface to the data. First, there should be a text document describing the data, addressing at least the following issues:
- general information on the language, e.g. fieldwork location, number of speakers, sociolinguistic situation, etc.
- scientific background/research field of researcher
- editorial background/rationale of the data
- selection criteria for entries, e.g. sampling, semantic fields, wordlists, etc.
- links to other databases/sources
Second, there should be various structured documents describing the structure of the data.
- description of data categories (e.g. ODD specification from TEI, other kind of database schema)
- specification of orthography used
- specification of terminology used
Possible Content providers
- Fieldworkers attached to MPI-EVA (Leipzig) and MPI for Psycholinguistics (Nijmegen)
- Lexical collections available online
- Intercontinental Dictionary Series, Loanword Typology Project (Leipzig)
Infrastructure[edit]
Social Issues
- advisory board for the whole Living Sources
- technical board for Living Sources in Lexical Description
- editorial board for Dictionaries of the world's languages
- convince the field: workshops at conferences, invite possible participants
- launch important: there has to be content available (prominent names in both the boards and the authors)
- get citation-style into LSA stylesheet
Technical issues
To be worked out in detail:
- Formats (TMF, LMF, TEI/dic.)
- Technical infrastructure: Lexus, eSciDoc
- Import from community formats, e.g. ToolBox
- Webservices, "command-line" expert access, API for outside access
- Searching the data: either graph search (through translational equivalents) or string based (through orthography profiles)
- Limited online editing, normally uploading of new version (diff check!)
- Unique identification structure for all data objects
- Direct reusability of data in local databases (linking of personal databases to online version, personal copies for offline usage)
- Formats for third party commentaries
- Formats for orthography profiles
- Formats to structurally capture the terminology used
Rights
- Open Access
- Creative Commons Licence for data and metadata (by default: attribution)
- Possibly different licenses for the different stages of the submission
- No copyright transfer
- agreement with authors that Living Sources in Lexical Description has the rights (to store) and distribute the data under the Creative Commons Licence
Miscellaneous
- Living Reviews infrastructure for the peer review might be re-used
- applied for domains livingsources.org, livingsources.com, livingsources.eu (request processed by AEI Potsdam)
Application[edit]
This initiative is planned as a three-year project, running from 01.07.09 until 31.06.2012.
Work Schedule[edit]
Phase 0: Preparations[edit]
from funding decision until projected start dat of 31.06.09
- recruiting of staff, setting up of offices
- community building: presentation and discussion of project at DoBeS meeting (a primary source of contributors)
- constitutions of boards:
- Advisory Board for the overarching framework of Living Sources
- Technical Board for Living Sources in Lexical Description
- Editorial Board for Dictionaries of the World's Languages
Phase 1: Concepts and Functional Specification[edit]
6 months: 01.07.09 - 31.12.09
- The various Board develop policies and concrete specifications for submissions and review
- Continue community building
- Agreement of encoding standards and metadata requirements
- Analysis of use cases and formulation of functional requirements for underlying framework
- Draft prototype of framework
- Functional specification and draft version of Graphical User Interface
Phase 2a: Prototype Implementation[edit]
12 months: 01.01.10 - 31.12.10
- Linking framework and GUI
- Adding functions for content evaluation, according to the specification as formulated by the Boards
- Adding data import/export functionality (ingestion, upload, conversion, versioning, download)
- Adding Web 2.0 functionality (user profiles, annotations, discussion)
- Adding citation structure (notes to users, receipts of downloads, custom save-sets)
Phase 2b: Final Implementation[edit]
6 months: 01.01.11 - 31.06.11
- Testing and validation
- Additions based on requests from beta-users
- Possibly inclusion of mirror of data from other data-repositories
- Possibly inclusion of special output formats, e.g. suitable for printing, or for websites
Phase 3: Data Ingestion[edit]
12 months: 01.07.11 - 31.06.12
- Marketing and dissemination of project to content providers and users
- Assistance with the first batch of ingestion of data
- Publication of guidelines and recommendations for content providers, users (both individuals and institutional, e.g. traditional journals), and funding agencies.
- Sustainability: organization of further financing of the framework and the data already ingested
Staff[edit]
- 1 Lexical Curator (TVöD ???)
- 2 Infrastructure Programmers (2 x TVöD ???)
- 1 Linguistic Assistant (half TVöD ???)
- 2 Student Assistants, one from linguistics and one from computer science
Expenses[edit]
- Dedicated development server (automatically covered by MPDL ???)
- Offices for staff (automatically covered by MPDL ???)
- Travel expenses for staff and visitors (EUR 10.000 per year)
This project depends to a large extent on the communication and cooperation with various partners, both developers at the MPDL in Munich and Berlin and at the MPIs in Leipzig and Nijmegen, as well as editors and content providers throughout the world. Success of this project strongly depends on regular meetings between the staff of the current project and these partners. To ensure this communication, we plan the following travel expenses:
- Visits to Nijmegen, Leipzig, Berlin and München to coordinate efforts with local developments (3 regional persons/trips per quarter, train and housing à 250,- = total 3.000,-per year)
- Visits to meetings of scientific community (conferences, workshops) to present and discuss the project (2 international persons/trips per year, flight and housing à 1.000,- = total 2.000,- per year)
- Workshops for community building (1 workshop per year, covering travel and housing for 5-10 international participants from outside the MPG à 5000,- = total 5.000,- per year)
Scientific Support within MPG[edit]
[Note: This is list is for planning only; not all of these people are contacted yet!]
MPG Directors
- Bernard Comrie/Martin Haspelmath (MPI-EVA Leipzig)
- Steve Levinson (MPI Psycholinguistics Nijmegen)
- Wolfgang Klein (MPI Psycholinguistics Nijmegen)
- Mike Tomasello/Elena Lieven (MPI-EVA Leipzig)
- Jürgen Renn (MPI History of Sciences Berlin)
- Jürgen Jost (MPI MiS Leipzig)
PMG Nachwuchsgruppenleiter
- Ina Bornkessel (MPI-CBS Leipzig)
- Michael Dunn (MPI Psycholinguistics Nijmegen)
- Brigitte Pakendorf (MPI-EVA Leipzig)
Cooperation[edit]
- DoBeS
- EMELD
- SIL
- DELAMAN
- LinguistList
Other Support[edit]
Potential subsidiary financial support:
- ESF call BABEL
- Volkswagenstiftung
- Heinz-Nixdorf-Stiftung
Subsidiary Information[edit]
The following information is not directly intended to end up in the application. It is just collected here for future reference.
Slides of meetings
On 30 September/1 October 2008 we had a meeting at the MPDL offices in Berlin to talk about a first draft of the application. These are a few of the slides that were presented to focus the discussion.
- Michael Cysouw File:Cysouw.pdf
- Dafydd Gibbon File:Gibbon.pdf
- Nikolaus Himmelmann File:Himmelmann.ppt
- Frank Seifart File:Seifart.doc